The Oxus region is home to archaeological relics of grand civilisations, most notably of ancient Bactria, but also of Chorasmia, Sogdiana, Margiana, and Hyrcania. However, most of these ruined sites enjoy far less fame, and are far less well-studied, than comparable relics in other parts of the world.
I recently watched an excellent documentary series called Alexander's Lost World, which investigates the history of the Oxus region in-depth, focusing particularly on the areas that Alexander the Great conquered as part of his legendary military campaign. I was blown away by the gorgeous scenery, the vibrant cultural legacy, and the once-majestic ruins that the series featured. But, more than anything, I was surprised and dismayed at the extent to which most of the ruins have been neglected by the modern world – largely due to the region's turbulent history of late.
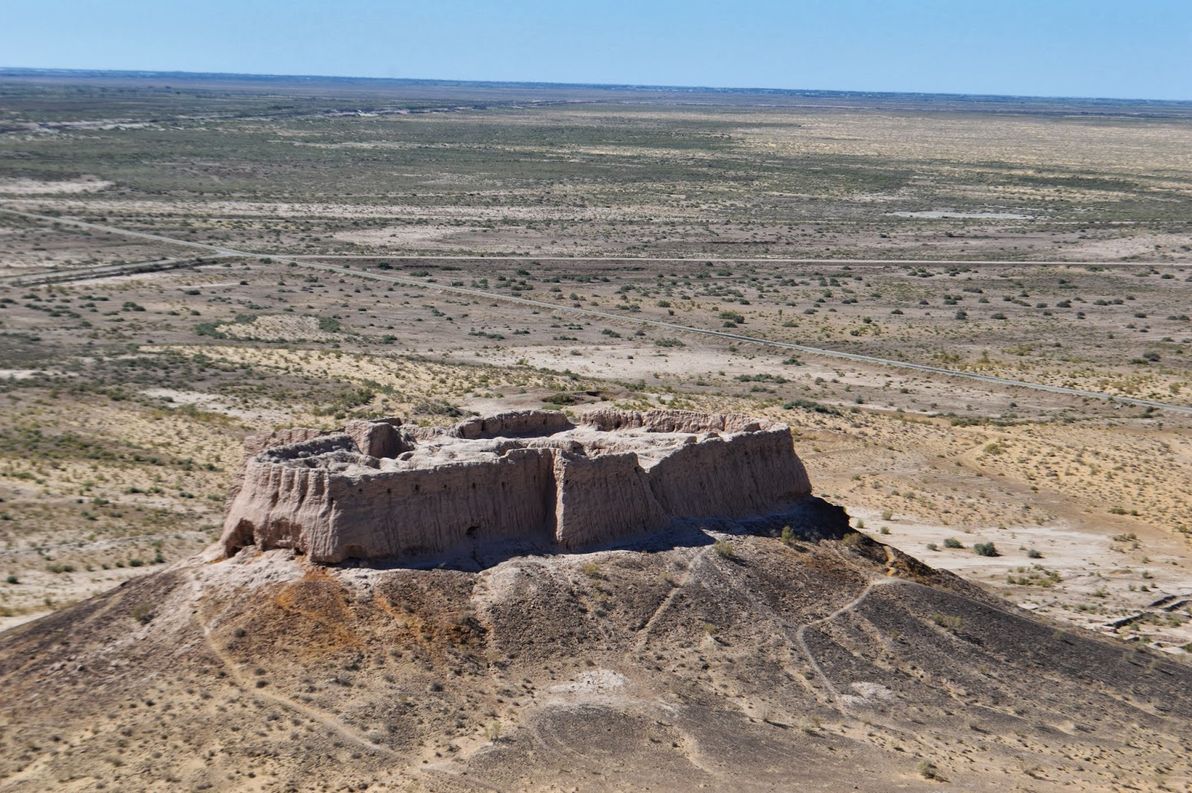

Image source: Stantastic: Back to Uzbekistan (Khiva).
This article has essentially the same aim as that of the documentary: to shed more light on the ancient cities and fortresses along the Oxus and nearby rivers; to get an impression of the cultures that thrived there in a bygone era; and to explore the climate change and the other forces that have dramatically affected the region between then and now.
Getting to know the rivers
First and foremost, an overview of the major rivers in question. Understanding the ebbs and flows of these arteries is critical, as they are the lifeblood of a mostly arid and unforgiving region.
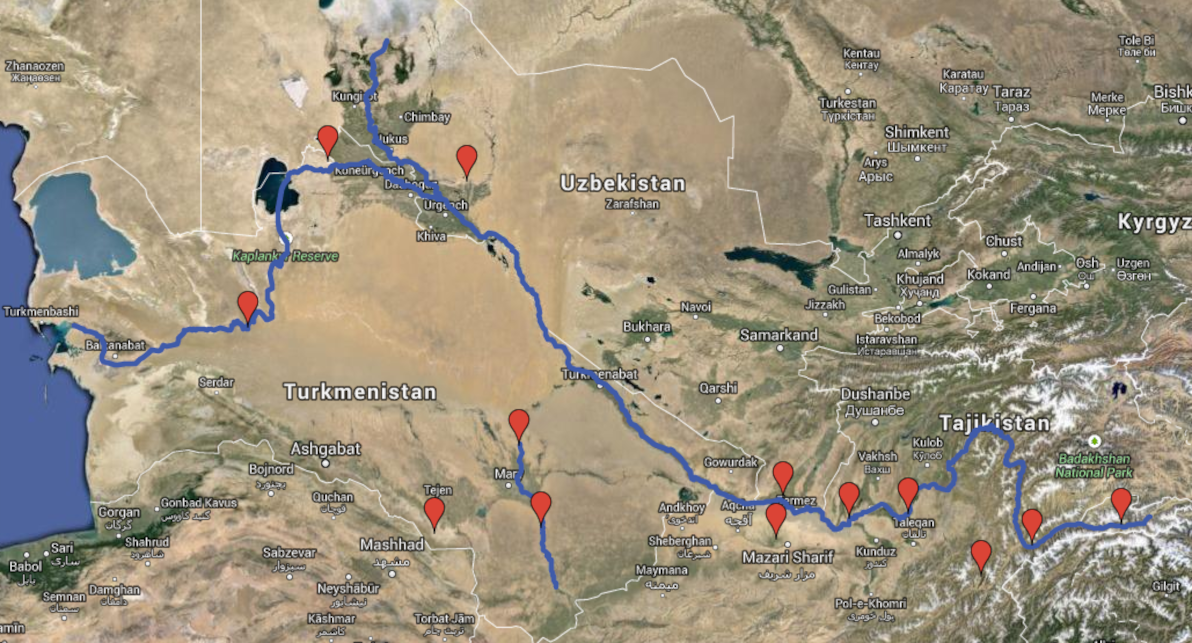
Map: Forgotten realms of the Oxus region (Google Maps Engine). Satellite imagery courtesy of Google Earth.
The Oxus is the largest river (by water volume) in Central Asia. Due to various geographical factors, it's also changed its course more times (and more dramatically) than any other river in the region, and perhaps in the world.
The source of the Oxus is the Wakhan river, which begins at Baza'i Gonbad at the eastern end of Afghanistan's remote Wakhan Corridor, often nicknamed "The Roof of the World". This location is only 40km from the tiny and seldom-crossed Sino-Afghan border. Although the Wakhan river valley has never been properly "civilised" – neither by ancient empires nor by modern states (its population is as rugged and nomadic today as it was millenia ago) – it has been populated continuously since ancient times.
Next in line downstream is the Panj river, which begins where the Wakhan and Pamir rivers meet. For virtually its entire length, the Panj follows the Afghanistan-Tajikistan border; and it winds a zig-zag course through rugged terrain for much of its course, until it leaves behind the modern-day Badakhstan province towards its end. Like the Wakhan, the mountainous upstream part of the Panj was never truly conquered; however, the more accessible downstream part was the eastern frontier of ancient Bactria.
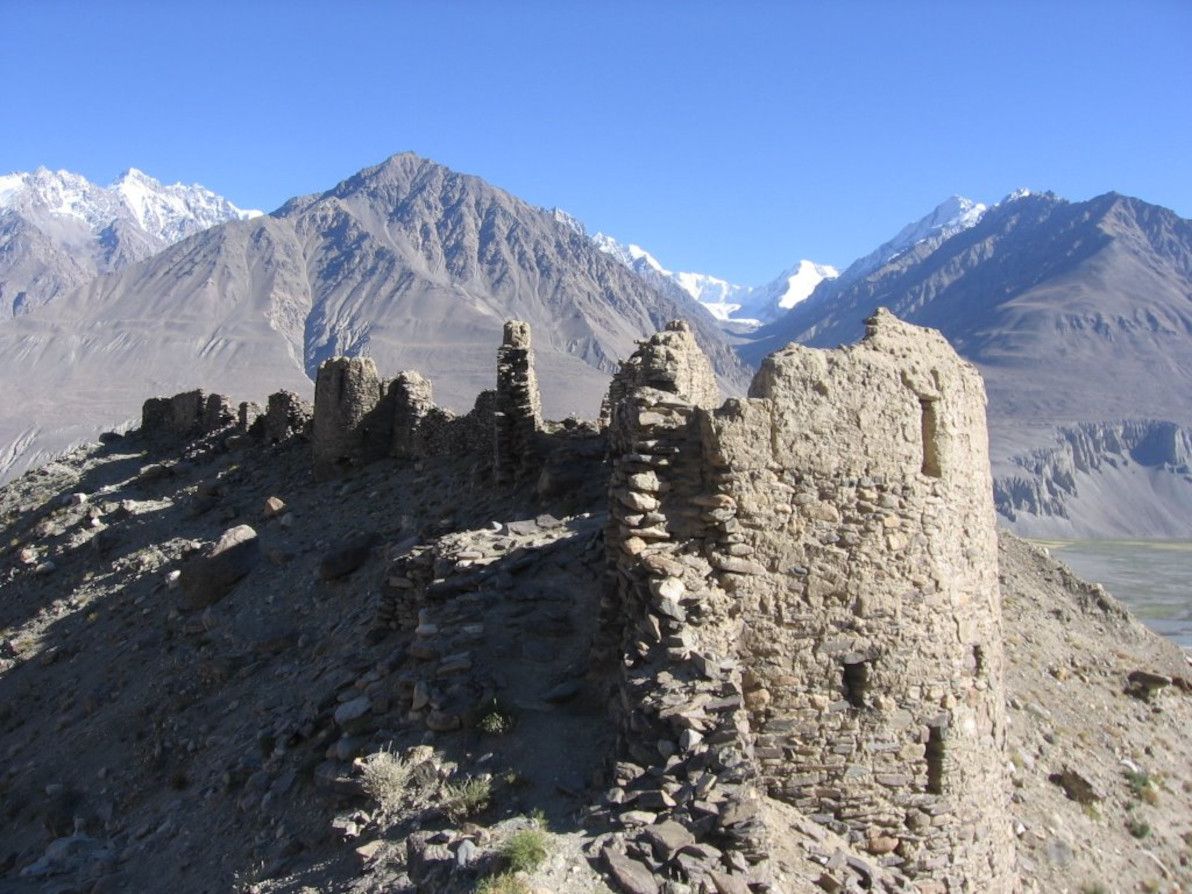

Image soure: Photos Khandud (Hava Afghanistan).
The Oxus proper begins where the Panj and Vakhsh rivers meet, on the Afghanistan-Tajikistan border. It continues along the Afghanistan-Uzbekistan border, and then along the Afghanistan-Turkmenistan border, until it enters Turkmenistan where the modern-day Karakum Canal begins. The river's course has been fairly stable along this part of the route throughout recorded history, although it has made many minor deviations, especially further downstream where the land becomes flatter. This part of the river was the Bactrian heartland in antiquity.
The rest of the river's route – mainly through Turkmenistan, but also hugging the Uzbek border in sections, and finally petering out in Uzbekistan – traverses the flat, arid Karakum Desert. The course and strength of the river down here has changed constantly over the centuries; for this reason, the Oxus has earned the nickname "the mad river". In ancient times, the Uzboy river branched off from the Oxus in northern Turkmenistan, and ran west across the desert until (arguably) emptying into the Caspian Sea. However, the strength of the Uzboy gradually lessened, until the river completely perished approximately 400 years ago. It appears that the Uzboy was considered part of the Oxus (and was given no name of its own) by many ancient geographers.
The Oxus proper breaks up into an extensive delta once in Uzbekistan; and for most of recorded history, it emptied into the Aral Sea. However, due to an aggressive Soviet-initiated irrigation campaign since the 1950s (the culmination of centuries of Russian planning and dreaming), the Oxus delta has rescinded significantly, and the river's waters fizzle out in the desert before reaching the sea. This is one of the major causes of the death of the Aral Sea, one of the worst environmental disasters on the planet.
Although geographically separate, the nearby Murghab river is also an important part of the cultural and archaeological story of the Oxus region (its lower reaches in modern-day Turkmenistan, at least). From its confluence with the Kushk river, the Murghab meanders gently down through semi-arid lands, before opening into a large delta that fans out optimistically into the unforgiving Karakum desert. The Murghab delta was in ancient times the heartland of Margiana, an advanced civilisation whose heyday largely predates that of Bactria, and which is home to some of the most impressive (and under-appreciated) archaeological sites in the region.
I won't be covering it in this article, as it's a whole other landscape and a whole lot more history; nevertheless, I would be remiss if I failed to mention the "sister" of the Oxus, the Syr Darya river, which was in antiquity known by its Greek name as the Jaxartes, and which is the other major artery of Central Asia. The source of the Jaxartes is (according to some) not far from that of the Oxus, high up in the Pamir mountains; from there, it runs mainly north-west through Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and then (for more than half its length) Kazakhstan, before approaching the Aral Sea from the east. Like the Oxus, the present-day Jaxartes also peters out before reaching the Aral; and since these two rivers were formerly the principal water sources of the Aral, that sea is now virtually extinct.
Hyrcania
Having finished tracing the rivers' paths from the mountains to the desert, I will now – Much like the documentary – explore the region's ancient realms the other way round, beginning in the desert lowlands.
The heartland of Hyrcania (more often absorbed into a map of ancient Parthia, than given its own separate mention) – in ancient times just as in the present-day – is Golestan province, Iran, which is a fertile and productive area on the south-west shores of the Caspian. This part of Hyrcania is actually outside of the Oxus region, and so falls off this article's radar. However, Hyrcania extended north into modern-day Turkmenistan, reaching the banks of the then-flowing Uzboy river (which was ambiguously referred to by Greek historians as the "Ochos" river).
Settlements along the lower Uzboy part of Hyrcania (which was on occasion given a name of its own, Nesaia) were few. The most notable surviving ruin there is the Igdy Kala fortress, which dates to approximately the 4th century BCE, and which (arguably) exhibits both Parthian and Chorasmian influence. Very little is known about Igdy Kala, as the site has seldom been formally studied. The question of whether the full length of the Uzboy ever existed remains unresolved, particularly regarding the section from Sarykamysh Lake to Igdy Kala.
By including Hyrcania in the Oxus region, I'm tentatively siding with those that assert that the "greater Uzboy" did exist; if it didn't (i.e. if the Uzboy finished in Sarykamysh Lake, and if the "lower Uzboy" was just a small inlet of the Caspian Sea), then the extent of cultural interchange between Hyrcania and the actual Oxus realms would have been minimal. In the documentary, narrator David Adams is quite insistent that the Oxus was connected to the Caspian in antiquity, making frequent reference to the works of Patrocles; while this was quite convenient for the documentary's hypothesis that the Oxo-Caspian was a major trade route, the truth is somewhat less black-and-white.
Chorasmia
North-east of Hyrcania, crossing the lifeless Karakum desert, lies Chorasmia, better known for most of its history as Khwarezm. Chorasmia lies squarely within the Oxus delta; although the exact location of its capitals and strongholds has shifted considerably over the centuries, due to political upheavals and due to changes in the delta's course. In antiquity (particularly in the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE), Chorasmia was a vassal state of the Achaemenid Persian empire, much like the rest of the Oxus region; the heavily Persian-influenced language and culture of Chorasmia, which can still be faintly observed in modern times, harks back to this era.
This region was strongest in medieval times, and its medieval capital at the present-day ghost city of Konye-Urgench – known in its heyday as Gurganj – was Chorasmia's most significant seat of power. Gurganj was abandoned in the 16th century CE, when the Oxus changed course and left the once-fertile city and surrounds without water.
It's unknown exactly where antiquity-era Chorsamia was centred, although part of the ruins of Kyrk Molla at Gurganj date back to this period, as do part of the ruins of Itchan Kala in present-day Khiva (which was Khwarezm's capital from the 17th to the 20th centuries CE). Probably the most impressive and best-preserved ancient ruins in the region, are those of the Ayaz Kala fortress complex, parts of which date back to the 4th century BCE. There are numerous other "Kala" (the Chorasmian word for "fortress") nearby, including Toprak Kala and Kz'il Kala.
One of the less-studied sites – but by no means a less significant site – is Dev-kesken Kala, a fortress lying due west of Konye-Urgench, on the edge of the Ustyurt Plateau, overlooking the dry channel of the former upper Uzboy river. Much like Konye-Urgench (and various other sites in the lower Oxus delta), Dev-kesken Kala was abandoned when the water stopped flowing, in around the 16th century CE. The city was formerly known as Vazir, and it was a thriving hub of medieval Khwarezm. Also like other sites, parts of the fortress date back to the 4th century BCE.
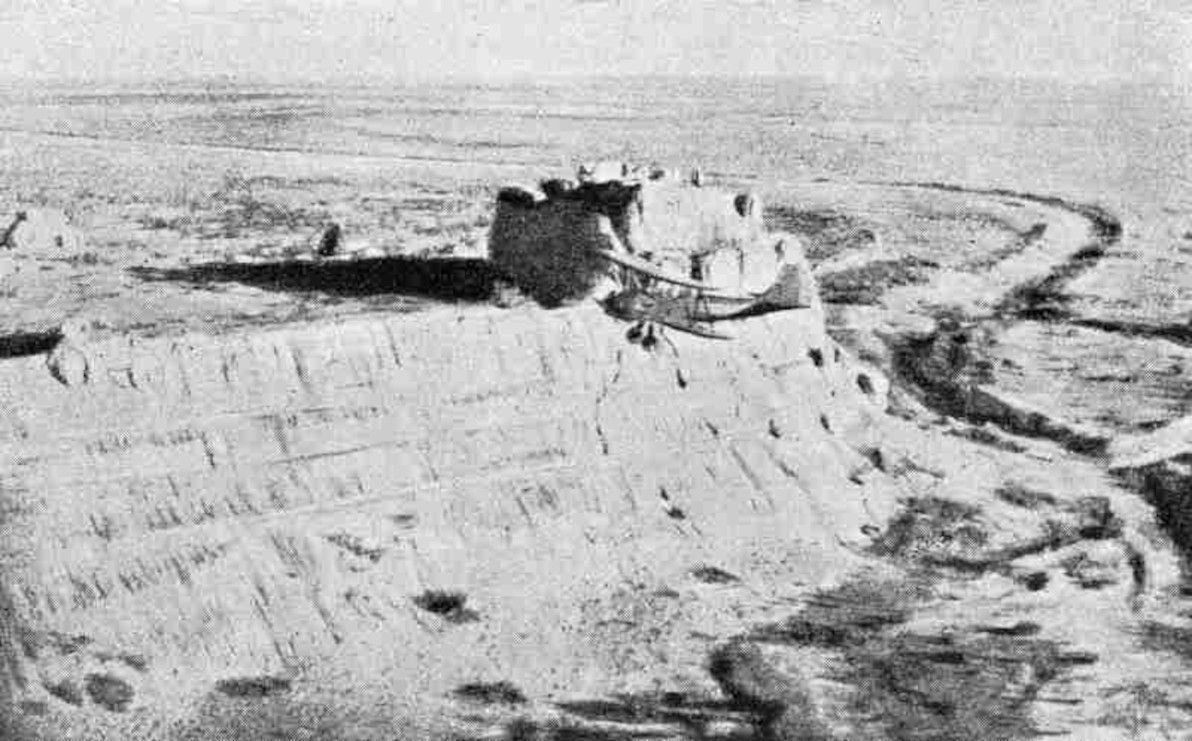

Image source: Karakalpak: Devkesken qala and Vazir.
I should also note that Dev-kesken Kala was one of the most difficult archaeological sites (of all the sites I'm describing in this article) to find information online for. I even had to create the Dev-Kesken Wikipedia article, which previously didn't exist (my first time creating a brand-new page there). The site was also difficult to locate on Google Earth (should now be easier, the co-ordinates are saved on the Wikipedia page). The site is certainly under-studied and under-visited, considering its distinctive landscape and its once-proud history; however, it is remote and difficult to access, and I understand that this Uzbek-Turkmen frontier area is also rather unsafe, due to an ongoing border dispute.
Margiana
South of Chorasmia – crossing the Karakum desert once again – one will find the realm that in antiquity was known as Margiana (although that name is simply the hellenised version of the original Persian name Margu). Much like Chorasmia, Margiana is centred on a river delta in an otherwise arid zone; in this case, the Murghab delta. And like the Oxus delta, the Murghab delta has also dried up and rescinded significantly over the centuries, due to both natural and human causes. Margiana lies within what is present-day southern Turkmenistan.
Although the Oxus doesn't run through Margiana, the realm is nevertheless part of the Oxus region (more surely so than Hyrcania, through which a former branch of the Oxus arguably runs), for a number of reasons. Firstly, it's geographically quite close to the Oxus, with only about 200km of flat desert separating the two. Secondly, the Murghab and the Oxus share many geographical traits, such as their arid deltas (as mentioned above), and also their habit of frequently and erratically changing course. Lastly, and most importantly, there is evidence of significant cultural interchange between Margiana and the other Oxus realms throughout civilised history.
The political centre of Margiana – in the antiquity period and for most of the medieval period, too – was the city of Merv, which was known then as Gyaur Kala (and also briefly by its hellenised name, Antiochia Margiana). Today, Merv is one of the largest and best-preserved archaeological sites in all the Oxus region, although most of the visible ruins are medieval, and the older ruins still lie largely buried underneath. The site has been populated since at least the 5th century BCE.
Although Merv was Margiana's capital during the Persian and Greek periods, the site of most significance around here is the far older Gonur Tepe. The site of Gonur was completely unknown to modern academics until the 1970s, when the legendary Soviet archaeologist Viktor Sarianidi discovered it (Sarianidi sadly passed away less than a year ago, aged 84). Gonur lies in what is today the parched desert, but what was – in Gonur's heyday, in approximately 2,000 BCE – well within the fertile expanse of the then-greater Murghab delta.
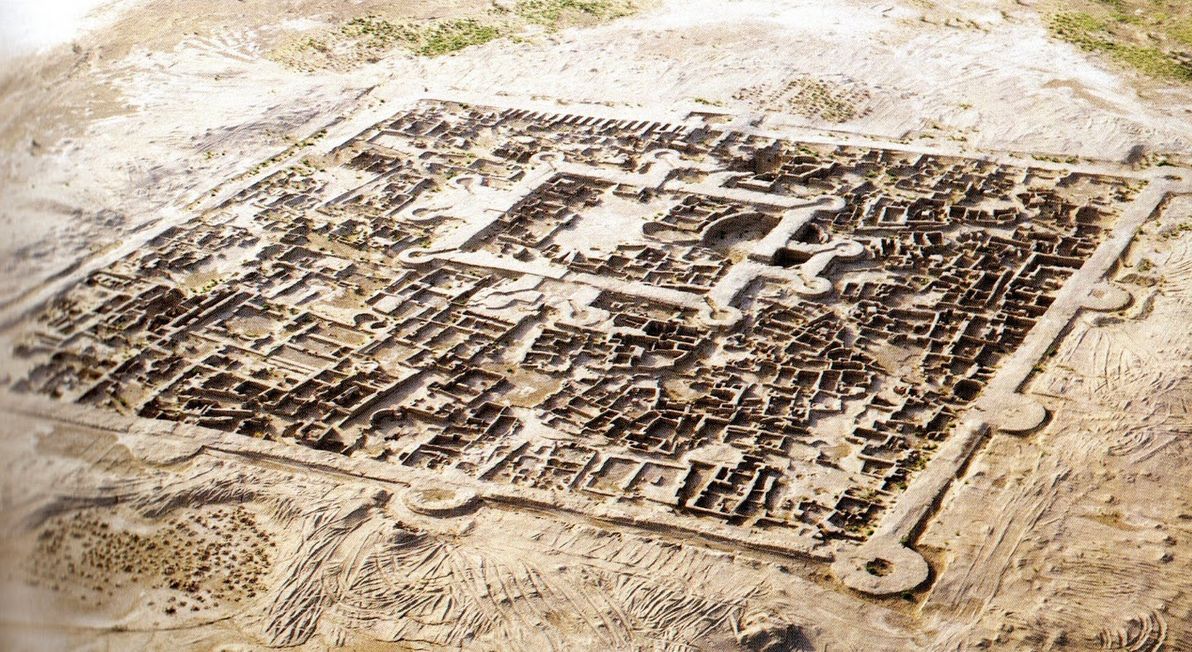

Image source: Boskawola.
Gonur was one of the featured sites in the documentary series – and justly so, because it's the key site of the so-called Bactria-Margiana Archaeological Complex. It's also a prime example of a "forgotten realm" in the region: to this day, few tourists and journalists have ever visited it (David Adams and his crew were among those that have made the arduous journey); and, apart from Sarianidi (who dedicated most of his life to studying Gonur and nearby ruins), few archaeologists have explored the site, and insufficient effort is being made by authorities and by academics to preserve the crumbling ruins. All this is a tragedy, considering that some have called for bronze-age Margiana to be added to the list of the classic "cradles of civilisation", which includes Egypt, Babylon, India, and China.
There are many other ruins in Margiana that were part of the bronze-age culture centred in Gonur. One of the other more promiment sites is Altyn Tepe, which lies about 200km south-west of Gonur, still within Turkmenistan but close to the Iranian border. Altyn Tepe, like Gonur, reached its zenith around 2,000 BCE; the site is characterised by a large Babylon-esque ziggurat. Altyn Tepe was also studied extensively by Sarianidi; and it too has been otherwise largely overlooked during modern times.
Sogdiana
Crossing the Karakum desert again (for the last time in this article) – heading north-east from Margiana – and crossing over to the northern side of the Oxus river, one may find the realm that in antiquity was known as Sogdiana (or Sogdia). Sogdiana principally occupies the area that is modern-day southern Uzbekistan and western Tajikistan.
The Sogdian heartland is the fertile valley of the Zeravshan river (old Persian name), which was once known by its Greek name, as the Polytimetus, and which has also been called the Sughd, in honour of its principal inhabitants (modern-day Tajikistan's Sughd province, through which the river runs, likewise honours them).
The Zeravshan's source is high in the mountains near the Tajik-Kyrgyz border, and for its entire length it runs west, passing through the key ancient Sogdian cities of Panjakent, Samarkand (once known as Maracanda), and Bukhara (which all remain vibrant cities to this day), before disappearing in the desert sands approaching the Uzbek-Turkmen border. The Zeravshan probably reached the Oxus and emptied into it – once upon a time – near modern-day Türkmenabat, which in antiquity was known as Amul, and in medieval times as Charjou. For most of its history, Amul lay just beyond the frontiers of Sogdiana, and it was the crossroads of all the principal realms of the Oxus region mentioned in this article.
Although Sogdiana is an integral part of the Oxus region, and although it was a dazzling civilisation in antiquity (indeed, it was arguably the most splendid of all the Oxus realms), I'm only mentioning it in this article for completeness, and I will refrain from exploring its archaeology in detail. (You may also have noted that the Zeravshan river and the Sogdian cities are missing from my custom map of the region). This is because I don't consider Sogdiana to be "forgotten", in anywhere near the sense that the other realms are "forgotten".
The key Sogdian sites – particularly Samarkand and Bukhara, which are both today UNESCO-listed – enjoy international fame; they have been studied intensively by modern academics; and they are the biggest tourist attractions in all of Central Asia. Apart from Sogdiana's prominence in Silk Road history, and its impressive and well-preserved architecture, the relative safety and stability of Uzbekistan – compared with its fellow Oxus-region neighbours Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Afghanistan – has resulted in the Sogdian heartland receiving the attention it deserves from the curious modern world.
Also – putting aside its "not forgotten" status – the partial exclusion (or, perhaps more accurately, the ambivalent inclusion) of Sogdiana from the Oxus region has deep historical roots. Going back to Achaemenid Persian times, Sogdiana was the extreme northern frontier of Darius's empire. And when the Greeks arrived and began to exert their influence, Sogdiana was known as Transoxiana, literally meaning "the land across the Oxus". Thus, from the point of view of the two great powers that dominated the region in antiquity – the Persians and the Greeks – Sogdiana was considered as the final outpost: a buffer between their known, civilised sphere of control; and the barbarous nomads who dwelt on the steppes beyond.
Bactria
Finally, after examining the other realms of the Oxus region, we come to the land that was the region's showpiece in the antiquity period: Bactria. The Bactrian heartland can be found south of Sogdiana, separated from it by the (relatively speaking) humble Chul'bair mountain range. Bactria occupies a prime position along the Oxus river: that is, it's the first section lying downstream of overly-rugged terrain; and it's upstream enough that it remains quite fertile to this day, although it's significantly less fertile than it was millennia ago. Bactria falls principally within modern-day northern Afghanistan; but it also encroaches into southern Uzbekistan and Tajikistan.
Historians know more about antiquity-era Bactria than they do about the rest of the Oxus region, primarily because Bactria was better incorporated into the great empires of that age than were its neighbours, and therefore far more written records of Bactria have survived. Bactria was a semi-autonomous satrapy (province) of the Persian empire since at least the 6th century BCE, although it was probably already under Persian influence well before then. It was conquered by Alexander the Great in 328 BCE (after he had already marched through Sogdiana the year before), thus marking the start of Greco-Bactrian rule, making Bactria the easternmost hellenistic outpost of the ancient world.
However, considering its place in the narrative of these empires, and considering its being recorded by both Persian and Greek historians, surprisingly little is known about the details of ancient Bactria today. This is why the documentary was called "Alexander's Lost World". Much like its neighbours, the area comprising modern-day Bactria is relatively seldom visited and seldom studied, due to its turbulent recent history.
The first archaeological site that I'd like to discuss in this section is that of Kampyr Tepe, which lies on the northern bank of the Oxus (putting it within Uzbek territory), just downstream from modern-day Termez. Kampyr Tepe was constructed around the 4th century BCE, possibly initially as a garrison by Alexander's forces. It was a thriving city for several centuries after that. It would have been an important defensive stronghold in antiquity, lying as it does near the western frontier of Bactria proper, not far from the capital, and affording excellent views of the surrounding territory.
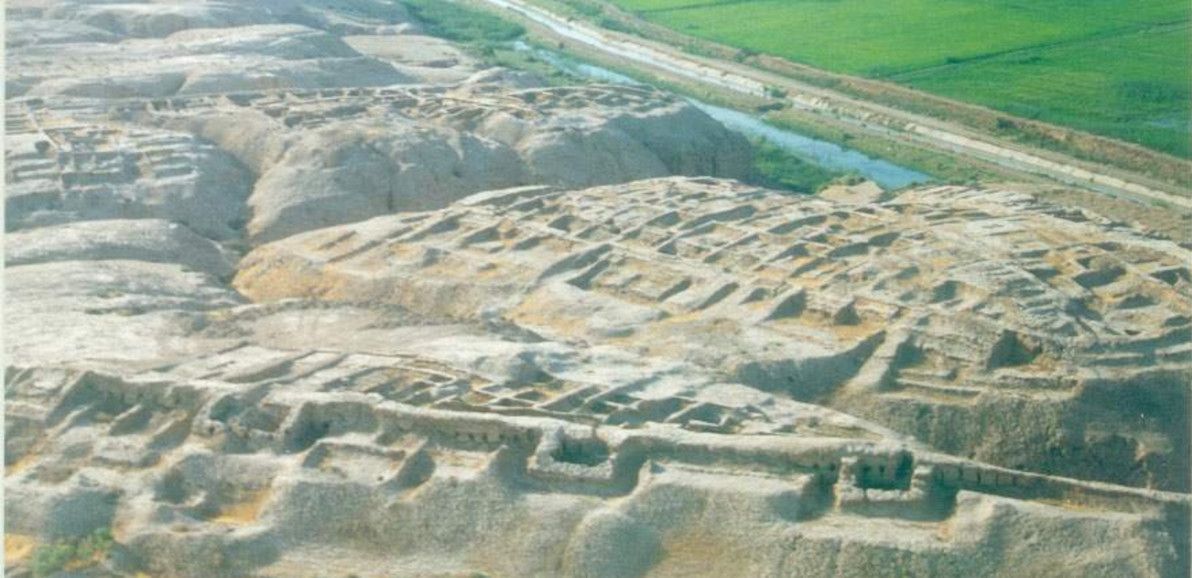

Image source: rusanoff – Photo of Kampyrtepa.
There is evidence that a number of different religious groups co-existed peacefully in Kampyr Tepe: relics of Hellenism, Zoroastrianism, and Buddhism from similar time periods have been discovered here. The ruins themselves are in good condition, especially considering the violence and instability that has affected the site's immediate surroundings in recent history. However, the reason for the site's admirable state of preservation is also the reason for its inaccessibility: due to its border location, Kampyr Tepe is part of a sensitive Uzbek military-controlled zone, and access is highly restricted.
The capital of Bactria was the grand city of Bactra, the location of which is generally accepted to be a circular plateau of ruins touching the northern edge of the modern-day city of Balkh. These lie within the delta of the modern-day Balkh river (once known as the Bactrus river), about 70km south of where the Oxus presently flows. In antiquity, the Bactrus delta reached the Oxus and fed into it; but the modern-day Balkh delta (like so many other deltas mentioned in this article) fizzles out in the sand.
Today, the most striking feature of the ruins is the 10km-long ring of thick, high walls enclosing the ancient city. Balkh is believed to have been inhabited since at least the 27th century BCE, although most of the archaeological remains only date back to about the 4th century BCE. The ruins at Balkh are currently on UNESCO's tentative World Heritage list. It's likely that the plateau at Balkh was indeed ancient Bactra; however, this has never been conclusively proven. Modern archaeologists barely had any access to the site until 2003, due to decades of military conflict in the area. To this day, access continues to be highly restricted, for security reasons.
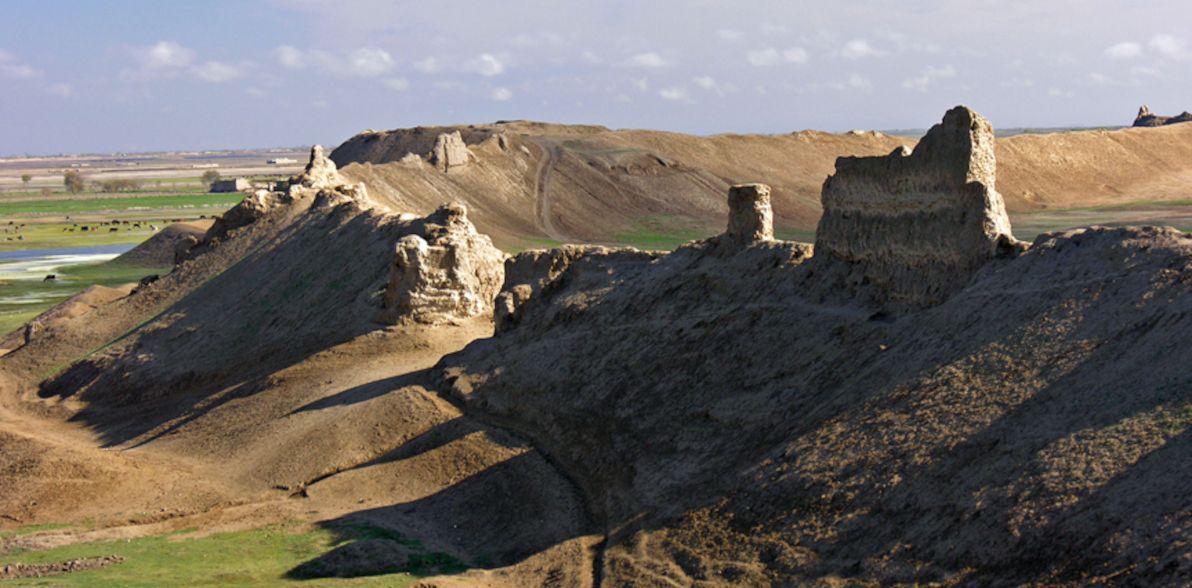

Image source: Hazara Association of UK.
Bactria was an important centre of Zoroastianism, and Bactra is one of (and is the most likely of) several contenders claiming to be the home of the mythical prophet Zoroaster. Tentatively related to this, is the fact that Bactra was also (possibly) once known as Zariaspa. A few historians have gone further, and have suggested that Bactra and Zariaspa were two different cities; if this is the case, then a whole new can of worms is opened, because it begs a multitude of further questions. Where was Zariaspa? Was Bactra at Balkh, and Zariaspa elsewhere? Or were Bactra and Zariaspa actually the same city… but located elsewhere?
Based on the theory of Ptolemy (and perhaps others), in the documentary David Adams strongly hypothesises that: (a) Bactra and Zariaspa were twin cities, next to each other; (b) the twin-city of Bactra-Zariaspa was located somewhere on the Oxus north of Balkh (he visits and proposes such a site, which I believe was somewhere between modern-day Termez and Aiwanj); and (c) this site, rather than Balkh, was the capital of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom that followed Alexander's conquest. While this is certainly an interesting hypothesis – and while it's true that there hasn't been nearly enough excavation or analysis done in modern times to rule it out – the evidence and the expert opinion, as it stands today, would suggest that Adams's hypothesis is wrong. As such, I think that his assertion of "the lost city of Bactra-Zariaspa" lying on the Oxus, rather than in the Bactrus delta, was stated rather over-confidently and with insufficient disclaimers in the documentary.
Upper Bactria
Although not historically or culturally distinct from the Bactrian heartland, I'm analysing "Upper Bactria" (i.e. the part of Bactria upstream of modern-day Balkh province) separately here, primarily to maintain structure in this article, but also because this farther-flung part of the realm is geographically quite rugged, in contrast to the heartland's sweeping plains.
First stop in Upper Bactria is the archaeological site of Takhti Sangin. This ancient ruin can be found on the Tajik side of the border; and since it's located at almost the exact spot where the Panj and Vakhsh rivers meet to become the Oxus, it could also be said that Takhti Sangin is the last site along the Oxus proper that I'm examining. However, much like the documentary, I'll be continuing the journey further upstream to the (contested) "source of the Oxus".
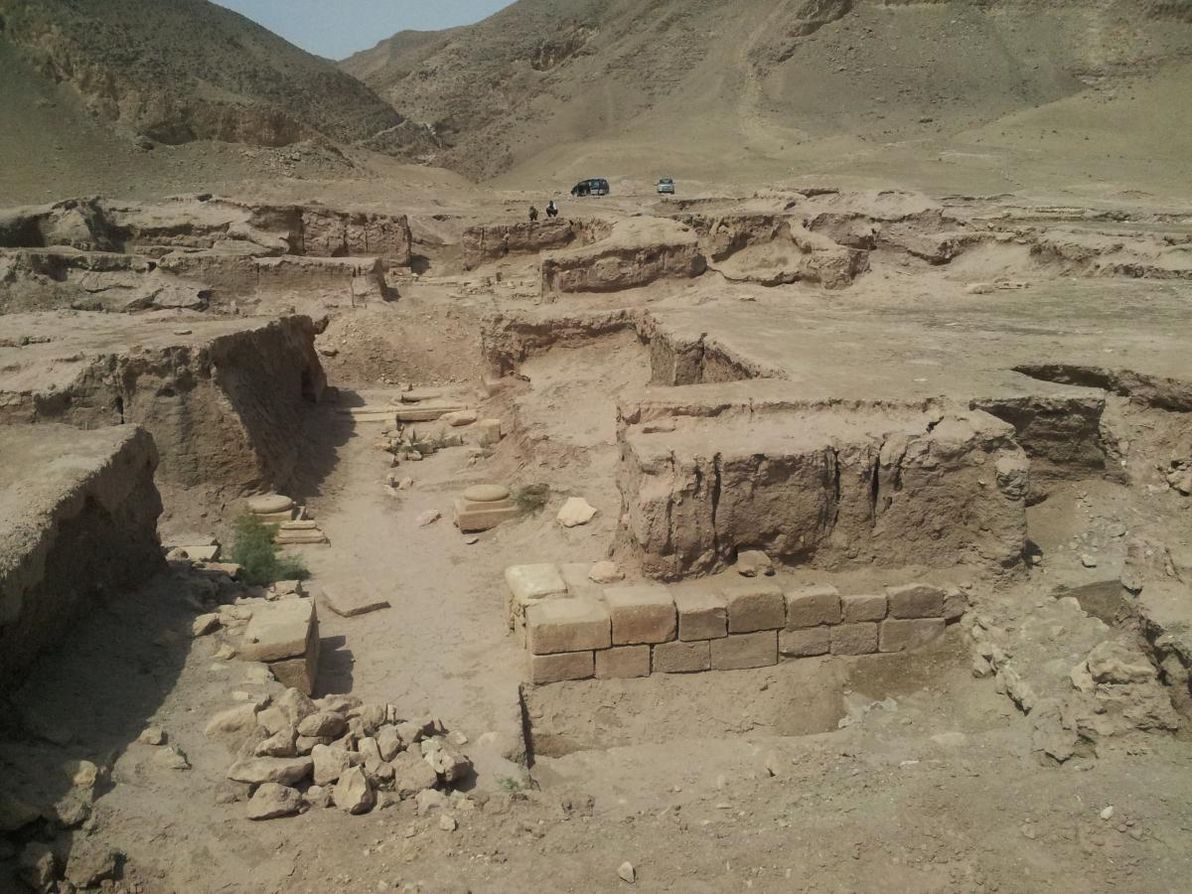

Image source: MATT: From North to South.
The principal structure at Takhti Sangin was a large Zoroastrian fire temple, which in its heyday boasted a pair of constantly-burning torches at its main entrance. Most of the remains at the site date back to the 3rd century BCE, when it became an important centre in the Greco-Bactrian kingdom (and when it was partially converted into a centre of Hellenistic worship); but the original temple is at least several centuries older than this, as attested to by various Achaemenid Persian-era relics.
Takhti Sangin is also the place where the famous "Oxus treasure" was discovered in the British colonial era (most of the treasure can be found on display at the British Museum to this day). In the current era, visitor access to Takhti Sangin is somewhat more relaxed than is access to the Bactrian sites further downstream (mentioned above) – there appear to be tour operators in Tajikistan running regularly-scheduled trips there – but this is also a sensitive border area, and as such, access is controlled by the Tajik military (who maintain a constant presence). Much like the sites of the Bactrian heartland, Takhti Sangin has been studied only sporadically by modern archaeologists, and much remains yet to be clarified regarding its history.
Moving further upstream, to the confluence of the Panj and Kokcha rivers, one reaches the site of Ai-Khanoum (meaning "Lady Moon" in modern Uzbek), which is believed (although not by all) to be the legendary city that was known in antiquity as Alexandria Oxiana. This was the most important Greco-Bactrian centre in Upper Bactria: it was built in the 3rd century BCE, and appears to have remained relatively vibrant for several centuries thereafter. It's also the site furthest upstream on the Oxus, for which there is significant evidence to indicate a Greco-Bactrian presence. It's a unique site within the Oxus region, in that it boasts the typical urban design of a classical Greek city; it's virtually "a little piece of Greece" in Central Asia. It even housed an amphitheatre and a gymnasium.
Ai-Khanoum certainly qualifies as a "lost" city: it was unknown to all save some local tribespeople, until the King of Afghanistan chanced upon it during a hunting trip in 1961. Due primarily to the subsequent Afghan-Soviet war, the site has been poorly studied (and also badly damaged) since then. In the documentary, it's explained how (and illustrated with some impressive 3D animation) – according to some – the Greco-Bactrian city was built atop the ruins of an older city, probably of Persian origin, which was itself once a dazzling metropolis. The documentary also indicates that access to Ai-Khanoum is currently tricky, and must be coordinated with the Afghan military; the site itself is also difficult to physically reach, as it's basically an island amongst the rivers that converge around it, depending on seasonal fluctuations.
The final site that I'd like to discuss regarding the realm of Bactria, is that of Sar-i Sang (a name meaning "place of stone"). At this particularly remote spot in the mountains of Badakhstan, there barely exists a town, neither today nor in ancient times. The nearest settlement of any size is modern-day Fayzabad, the provincial capital. From Ai-Khanoum, the Kokcha river winds upstream and passes through Fayzabad; and from there, the Kokcha valley continues its treacherous path up into the mountains, with Sar-i Sang located about 100km's south of Fayzabad.
Sar-i Sang is not a town, it's a mine: at an estimated 7,000 years of age, it's believed to be the oldest continuously-operating mine in the world. Throughout recorded history, people have come here seeking the beautiful precious stone known as lapis lazuli, which exists in veins of the hillsides here in the purest form and in the greatest quantity known on Earth.
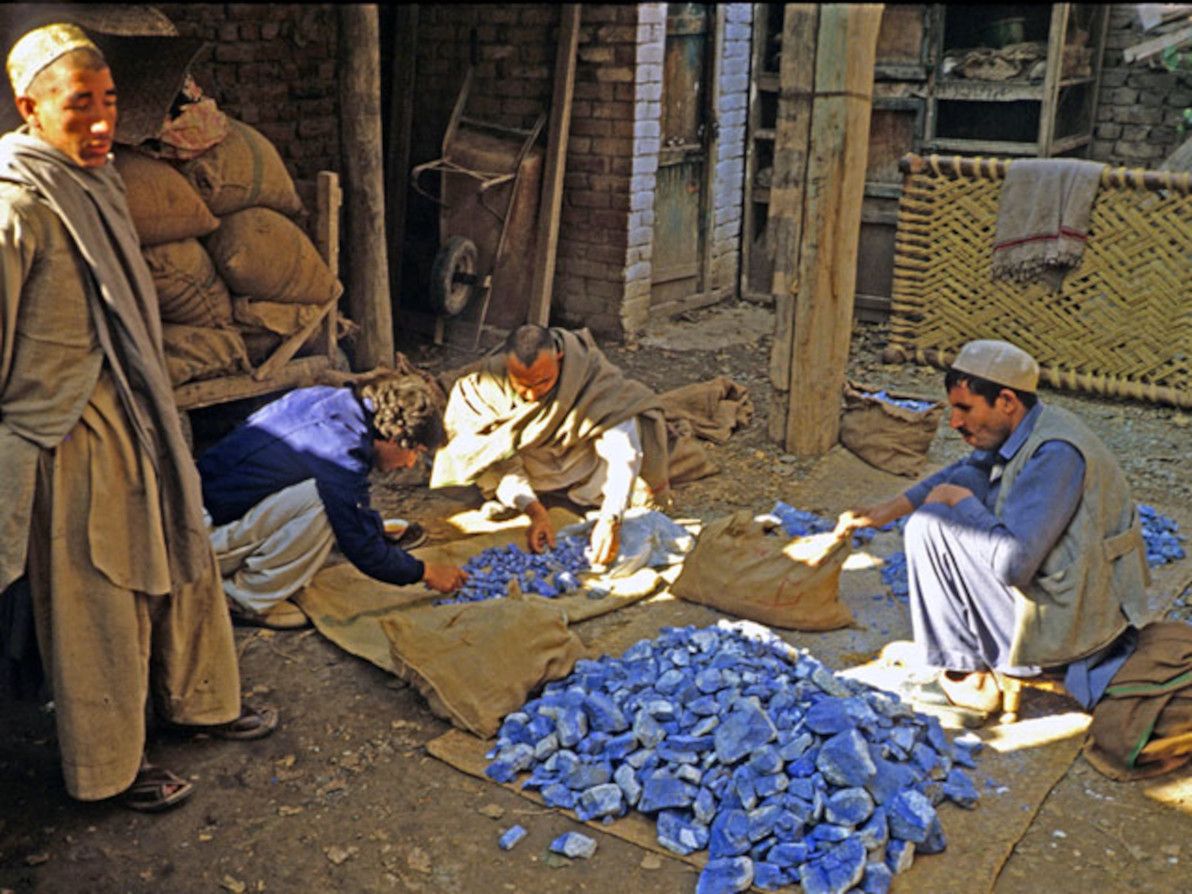

Image source: Jewel Tunnel Imports: Lapis Lazuli.
Although Sar-i Sang (also known as Darreh-Zu) is quite distant from all the settlements of ancient Bactria (and quite distant from the Oxus), the evidence suggests that throughout antiquity the Bactrians worked the mines here, and that lapis lazuli played a significant role in Bactria's international trade. Sar-i Sang lapis lazuli can be found in numerous famous artifacts of other ancient empires, including the tomb of Tutankhamun in Egypt. Sources also suggest that this distinctive stone was Bactria's most famous export, and that it was universally associated with Bactria, much like silk was associated with China.
The Wakhan
Having now discussed the ancient realms of the Oxus from all the way downstream in the hot desert plains, there remains only one segment of this epic river left to explore: its source far upstream. East of Bactria lies one of the most inaccessible, solitary, and unspoiled places in the world: the Wakhan Corridor. Being the place where a number of very tall mountain ranges meet – among them the Pamirs, the Hindu Kush, and the Karakoram – the Wakhan has often been known as "The Roof of the World".
The Wakhan today is a long, slim "panhandle" of territory within Afghanistan, bordered to the north by Tajikistan, to the south by Pakistan, and to the east by China. This distinctive borderline was a colonial-era invention, a product of "The Great Game" played out between Imperial Russia and Britain, designed to create a buffer zone between these powers. Historically, however, the Wakhan has been nomadic territory, belonging to no state or empire, and with nothing but the immensity of the surrounding geography serving as its borders (as it continues to be on the ground to this day). The area is also miraculously bereft of the scourges of war and terrorism that have plagued the rest of Afghanistan in recent years.
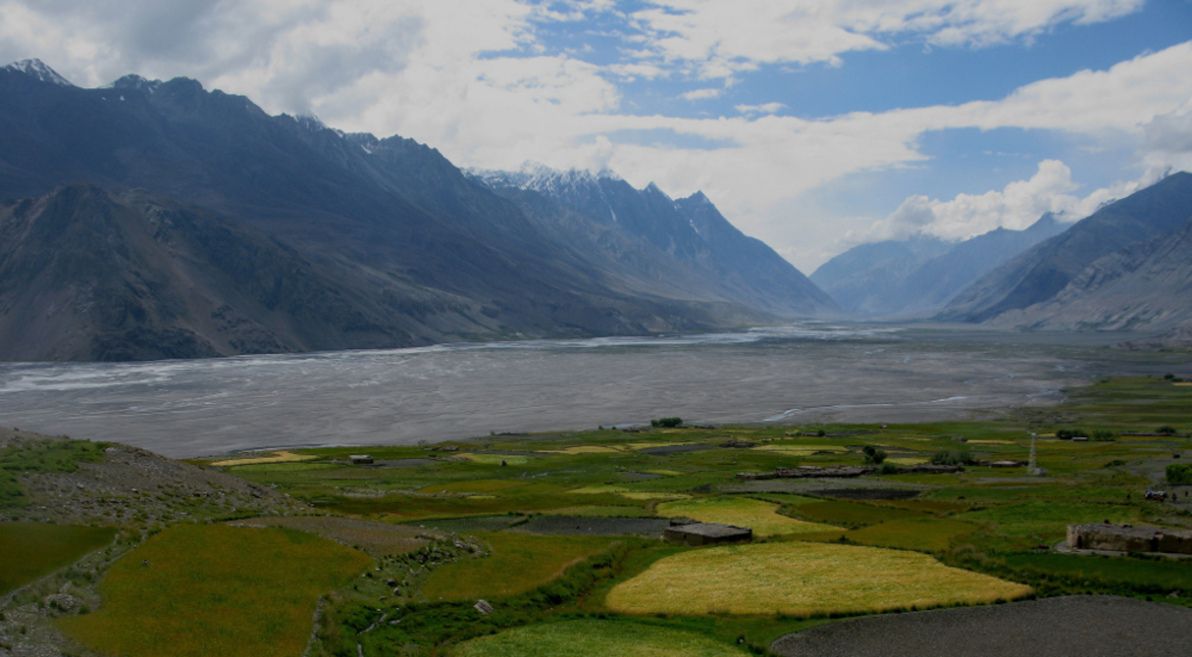

Image source: Geoffrey Degens: Wakhan Valley at Sarhad.
Much like the documentary, my reasons for discussing the Wakhan are primarily geographic ones. The Wakhan is centred around a single long valley, whose river – today known as the Panj, and then higher up as the Wakhan river – is generally recognised as the source of the Oxus. It's important to acknowledge this high-altitude area, which plays such an integral role in feeding the river that diverse cultures further downstream depend upon, and which has fuelled the Oxus's long and colourful history.
There are few significant archaeological sites within the Wakhan. The ancient Kaakha fortress falls just outside the Wakhan proper, at the extreme eastern-most extent of the influence of antiquity-era kingdoms in the Oxus region. The only sizeable settlement in the Wakhan itself is the village of Sarhad, which has been continuously inhabited for millennia, and which is the base of the unique Wakhi people, who are the Wakhan's main tribe (Sarhad is also where the single rough road along the Wakhan valley ends). Just next to Sarhad lies the Kansir fort, built by the Tibetan empire in the 8th century CE, a relic of the battle that the Chinese and Tibetan armies fought in the Wakhan in the year 747 CE (this was probably the most action that the Wakhan has ever seen in its history).
Close to the very spot where the Wakhan river begins is Baza'i Gonbad (or Bozai Gumbaz, in Persian "domes of the elders"), a collection of small, ancient mud-brick domes about which little is known. As there's nothing else around for miles, they are occasionally used to this day as travellers' shelters. They are believed to be the oldest structures in the Wakhan, but it's unclear who built them (it was probably one of the nomadic Kyrgyz tribes that roam the area), or when.
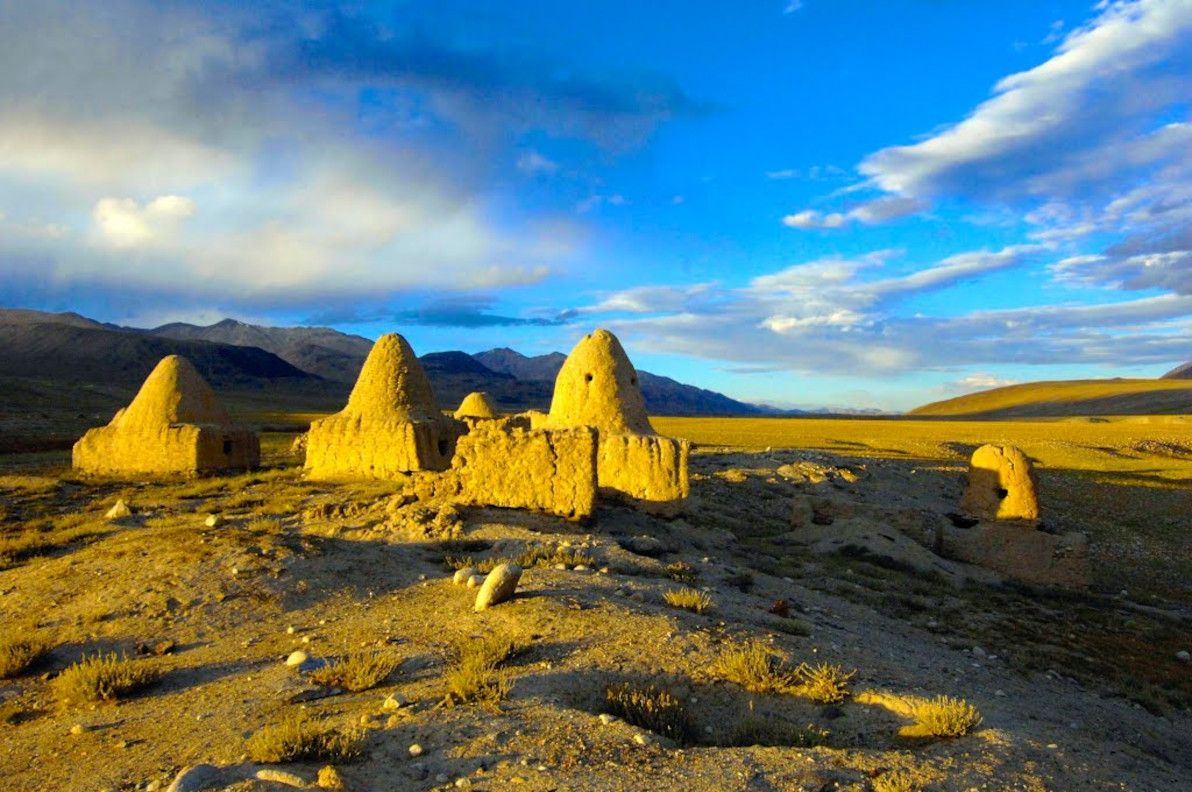

Image source: David Adams Films: Bozai Gumbaz.
Regarding which famous people have visited the Wakhan throughout history: it appears almost certain that Marco Polo passed through the Wakhan in the 13th century CE, in order to reach China; and a handful of other Europeans visited the Wakhan in the subsequent centuries (and it's almost certain that the only "tourists" to ever visit the Wakhan are those of the past century or so). In the documentary, David Adams suggests repeatedly in the final episode (that in which he journeys to the Wakhan) that Alexander – either the man himself, or his legions – not only entered the Wakhan Corridor, but even crossed one of its high passes over to Pakistan. I've found no source to clearly corroborate this claim; and after posing the question to a forum of Alexander-philes, it appears quite certain that neither Alexander nor his legions ever set foot in the Wakhan.
Conclusion
So, there you have it: my humble overview of the history of a region ruled by rivers, empires, and treasures. As I've emphasied throughout this article, the Oxus region is most lamentably a neglected and under-investigated place, considering its colourful history and its rich tapestry of cultures and landscapes. My aim in writing this piece is simply to inform anyone else who may be interested, and to better preserve the region's proud legacy.
I must acknowledge and wholeheartedly thank David Adams and his team for producing the documentary Alexander's Lost World, which I have referred to throughout this article, and whose material I have re-analysed as the basis of my writings here. The series has been criticised by history buffs for its various inaccuracies and unfounded claims; and I admit that I too, in this article, have criticised it several times. However, despite this, I laud the series' team for producing a documentary that I enjoyed immensely, and that educated me and inspired me to research the Oxus region in-depth. Like the documentary, this article is about rivers and climate change as the primary forces of the region, and Alexander the Great (along with other famous historical figures) is little more than a sidenote to this theme.
I am by no means an expert on the region, nor have I ever travelled to it (I have only "vicariously" travelled there, by watching the documentary and by writing this article!). I would love to someday set my own two feet upon the well-trodden paths of the Oxus realms, and to see these crumbling testaments to long-lost g-ds and kings for myself. For now, however, armchair history blogging will have to suffice.
]]>